
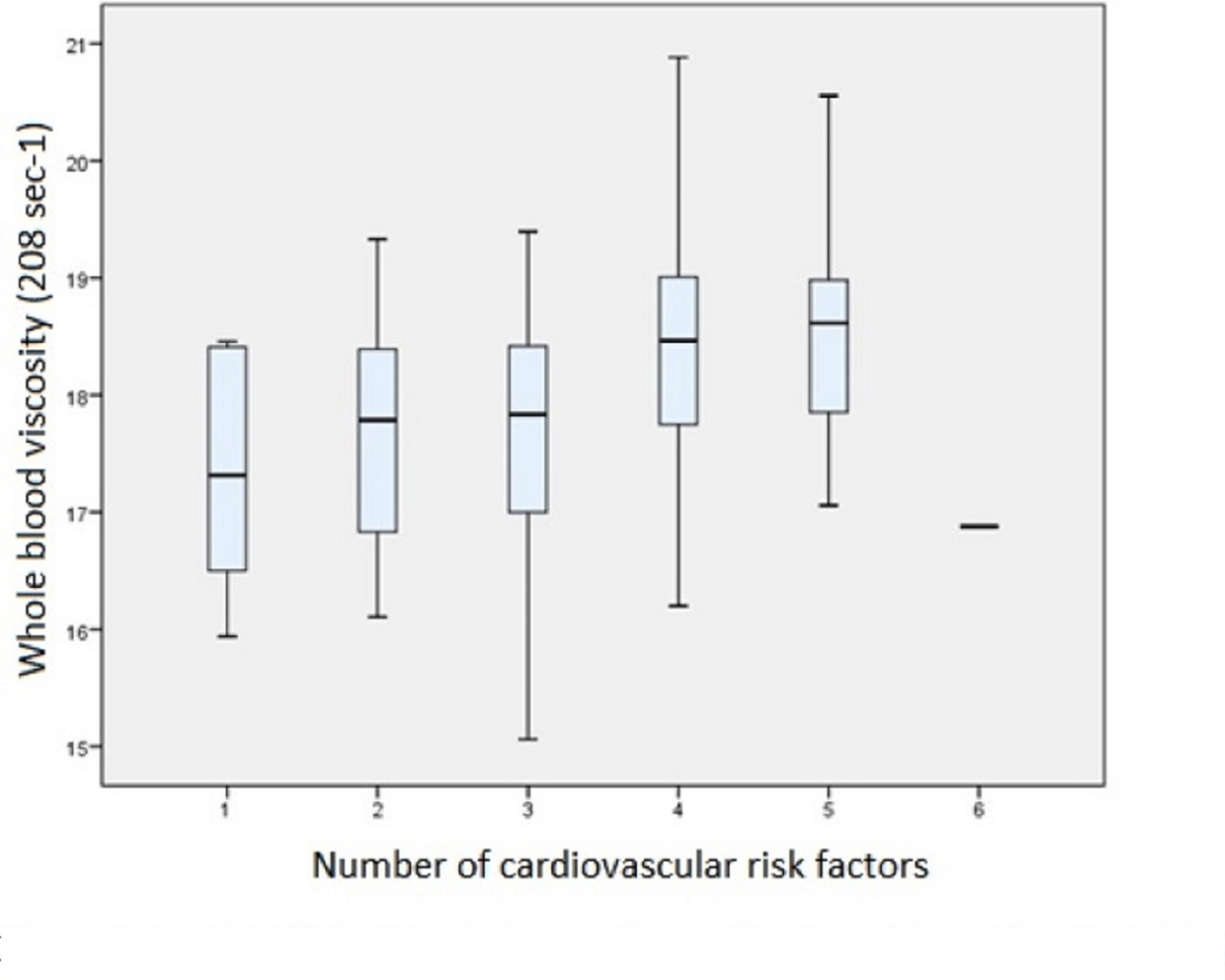
The basal ESR is slightly higher in females. This is especially likely with IgM-class paraproteins, and to a lesser extent, IgA-class. Although increases in immunoglobulins usually increase the ESR, very high levels can reduce it again due to hyperviscosity of the plasma. The ESR is decreased in polycythemia, hyperviscosity, sickle cell anemia, leukemia, chronic fatigue syndrome, low plasma protein (due to liver or kidney disease) and congestive heart failure. The ESR is increased in inflammation, pregnancy, anemia, autoimmune disorders (such as rheumatoid arthritis and lupus), infections, some kidney diseases and some cancers (such as lymphoma and multiple myeloma). While aggregation already takes place at normal physiological fibrinogen levels, these tend to increase when and inflammatory process is present, leading to increased ESR. As according to Stokes'_law the sedimentation velocity varies like the square of the object’s diameter, larger aggregates settle faster. The ESR is influenced by the aggregation of red blood cells: blood plasma proteins, mainly fibrinogen promote the formation of red cell clusters called rouleaux or larger structures (interconnected rouleaux, irregular clusters). Since the introduction of automated analyzers into the clinical laboratory, the ESR test has been automatically performed. To perform the test, anticoagulated blood is traditionally placed in an upright tube, known as a Westergren tube, and the distance which the red blood cells fall is measured and reported in millimetres at the end of one hour. It is a common hematology test, and is a non-specific measure of inflammation. The erythrocyte sedimentation rate ( ESR or sed rate) is the rate at which red blood cells in anticoagulated whole blood descend in a standardized tube over a period of one hour.
The millimeters of transparent fluid present at the top portion of the vertical tube after an hour.
The rate of sedimentation of erythrocytes in a vertical tube over an hour. Sedimentation rate, Westergren ESR, ESR, sed rate The ESR is the height (in mm) of the colourless portion at the top of the pipette after one hour. Westergren pipet array on StaRRsed automated ESR analyzer.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
